Cron Jobs
This guide shows how to use the Restate to schedule cron jobs.
A cron job is a scheduled task that runs periodically at a specified time or interval. It is often used for background tasks like cleanup or sending notifications.
Restate has no built-in functionality for cron jobs. But Restate's durable building blocks make it easy to implement a service that does this for us, and uses the guarantees Restate gives to make sure tasks get executed reliably.
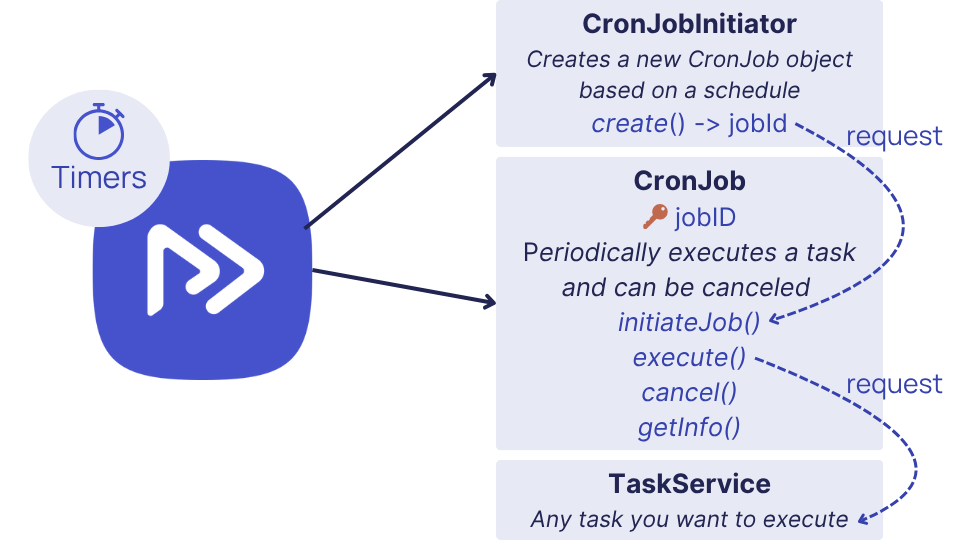
Restate has many features that make it a good fit for implementing cron jobs:
- Durable timers: Schedule tasks to run at a specific time in the future. Restate ensures execution.
- Task resiliency: Restate ensures that tasks are retried until they succeed.
- Task control: Cancel and inspect running jobs.
- K/V state: We store the details of the cron jobs in Restate, so we can retrieve them later and query them from the outside.
- FaaS support: Run your services on FaaS infrastructure, like AWS Lambda. Restate will scale your scheduler and tasks to zero while they sleep.
- Scalability: Restate can handle many cron jobs running in parallel, and can scale horizontally to handle more load.
- Observability: See the execution history of the cron jobs, and their status in the Restate UI.
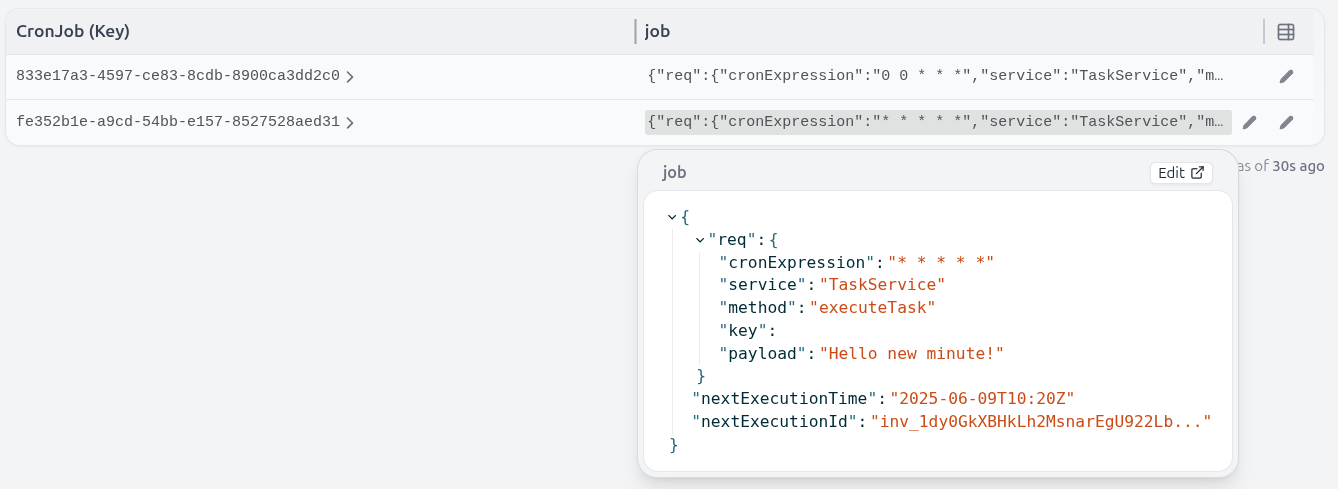
Example
The example implements a cron service that you can copy over to your own project.
Usage:
- Send requests to
CronJobInitiator.create()to start new jobs with standard cron expressions:{"cronExpression": "0 0 * * *", # E.g. run every day at midnight"service": "TaskService", # Schedule any Restate handler"method": "executeTask","key": "taskId", # Optional, Virtual Object key"payload": "Hello midnight!"} - Each job gets a unique ID and runs as a CronJob virtual object
- Jobs automatically reschedule themselves after each execution
- TypeScript
- Java
export const cronJobInitiator = restate.service({name: "CronJobInitiator",handlers: {create: async (ctx: restate.Context, req: JobRequest) => {const jobId = ctx.rand.uuidv4();const job = await ctx.objectClient(cronJob, jobId).initiate(req);return `Job created with ID ${jobId} and next execution time ${job.next_execution_time}`;},},});export const cronJob = restate.object({name: "CronJob",handlers: {initiate: async (ctx: restate.ObjectContext, req: JobRequest): Promise<JobInfo> => {if (await ctx.get<JobInfo>(JOB)) {throw new TerminalError("Job already exists for this ID.");}return await scheduleNextExecution(ctx, req);},execute: async (ctx: restate.ObjectContext) => {const job = await ctx.get<JobInfo>(JOB);if (!job) {throw new TerminalError("Job not found.");}// execute the taskconst { service, method, key, payload } = job.req;if (payload) {ctx.genericSend({service,method,parameter: payload,key,inputSerde: serde.json,});} else {ctx.genericSend({service,method,parameter: undefined,key,inputSerde: serde.empty,});}await scheduleNextExecution(ctx, job.req);},cancel: async (ctx: restate.ObjectContext) => {// Cancel the next executionconst job = await ctx.get<JobInfo>(JOB);if (job) {ctx.cancel(job.next_execution_id);}// Clear the job statectx.clearAll();},getInfo: async (ctx: restate.ObjectSharedContext) => ctx.get<JobInfo>(JOB),},});const scheduleNextExecution = async (ctx: restate.ObjectContext,req: JobRequest): Promise<JobInfo> => {// Parse cron expression// Persist current date in Restate for deterministic replayconst currentDate = await ctx.date.now();let interval;try {interval = CronExpressionParser.parse(req.cronExpression, { currentDate });} catch (e) {throw new TerminalError(`Invalid cron expression: ${(e as Error).message}`);}const next = interval.next().toDate();const delay = next.getTime() - currentDate;// Schedule next executionconst handle = ctx.objectSendClient(cronJob, ctx.key, { delay }).execute();// Store the job informationconst job = {req,next_execution_time: next.toString(),next_execution_id: await handle.invocationId,};ctx.set<JobInfo>(JOB, job);return job;};
@Servicepublic static class JobInitiator {@Handlerpublic String create(Context ctx, JobRequest req) {var jobId = ctx.random().nextUUID().toString();var cronJob = CronJobClient.fromContext(ctx, jobId).initiate(req).await();return String.format("Job created with ID %s and next execution time %s", jobId, cronJob.nextExecutionTime());}}@Name("CronJob")@VirtualObjectpublic static class Job {private final StateKey<JobInfo> JOB = StateKey.of("job", JobInfo.class);private final CronParser PARSER =new CronParser(CronDefinitionBuilder.instanceDefinitionFor(UNIX));@Handlerpublic JobInfo initiate(ObjectContext ctx, JobRequest req) {if (ctx.get(JOB).isPresent()) {throw new TerminalException("Job already exists for this ID");}return scheduleNextExecution(ctx, req);}@Handlerpublic void execute(ObjectContext ctx) {JobRequest req = ctx.get(JOB).orElseThrow(() -> new TerminalException("Job not found")).req;executeTask(ctx, req);scheduleNextExecution(ctx, req);}@Handlerpublic void cancel(ObjectContext ctx) {ctx.get(JOB).ifPresent(job -> ctx.invocationHandle(job.nextExecutionId).cancel());// Clear the job statectx.clearAll();}@Sharedpublic Optional<JobInfo> getInfo(SharedObjectContext ctx) {return ctx.get(JOB);}private void executeTask(ObjectContext ctx, JobRequest job) {Target target =(job.key.isPresent())? Target.virtualObject(job.service, job.method, job.key.get()): Target.service(job.service, job.method);var request =(job.payload.isPresent())? Request.of(target, TypeTag.of(String.class), TypeTag.of(Void.class), job.payload.get()): Request.of(target, new byte[0]);ctx.send(request);}private JobInfo scheduleNextExecution(ObjectContext ctx, JobRequest req) {// Parse cron expressionExecutionTime executionTime;try {executionTime = ExecutionTime.forCron(PARSER.parse(req.cronExpression));} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {throw new TerminalException("Invalid cron expression: " + e.getMessage());}// Calculate next execution timevar now = ctx.run(ZonedDateTime.class, ZonedDateTime::now);var delay =executionTime.timeToNextExecution(now).orElseThrow(() -> new TerminalException("Cannot determine next execution time"));var next =executionTime.nextExecution(now).orElseThrow(() -> new TerminalException("Cannot determine next execution time"));// Schedule next executionvar handle = CronJobClient.fromContext(ctx, ctx.key()).send().execute(delay);// Save job statevar job = new JobInfo(req, next.toString(), handle.invocationId());ctx.set(JOB, job);return job;}}}
Adapt to your use case
Note that this implementation is fully resilient, but you might need to make some adjustments to make this fit your use case:
- Take into account time zones.
- Adjust how you want to handle tasks that fail until the next task gets scheduled. With the current implementation, you would have concurrent executions of the same cron job (one retrying and the other starting up).
Running the example
Download the example
- ts
- java
restate example typescript-patterns-use-cases && cd typescript-patterns-use-cases
restate example java-patterns-use-cases && cd java-patterns-use-cases
Start the Restate Server
restate-server
Start the Service
- ts
- java
npx tsx watch ./src/cron/task_service.ts
./gradlew -PmainClass=my.example.cron.TaskService run
Register the services
restate deployments register localhost:9080
Send a request
For example, run executeTask every minute:
- ts
- java
curl localhost:8080/CronJobInitiator/create --json '{"cronExpression": "* * * * *","service": "TaskService","method": "executeTask","payload": "Hello new minute!"}'
curl localhost:8080/CronJobInitiator/create --json '{"cronExpression": "* * * * *","service": "TaskService","method": "executeTask","payload": "Hello new minute!"}'
For example, or run executeTask at midnight:
- ts
- java
curl localhost:8080/CronJobInitiator/create --json '{"cronExpression": "0 0 * * *","service": "TaskService","method": "executeTask","payload": "Hello midnight!"}'
curl localhost:8080/CronJobInitiator/create --json '{"cronExpression": "0 0 * * *","service": "TaskService","method": "executeTask","payload": "Hello midnight!"}'
You can also use the cron service to execute handlers on Virtual Objects, by specifying the Virtual Object key in the request.
You will get back a response with the job ID.
Using the job ID, you can then get information about the job:
- ts
- java
curl localhost:8080/CronJob/myJobId/getInfo
curl localhost:8080/CronJob/myJobId/getInfo
Or cancel the job later:
- ts
- java
curl localhost:8080/CronJob/myJobId/cancel
curl localhost:8080/CronJob/myJobId/cancel
Check the scheduled tasks and state
In the UI, you can see how the tasks are scheduled, and how the state of the cron jobs is stored in Restate.
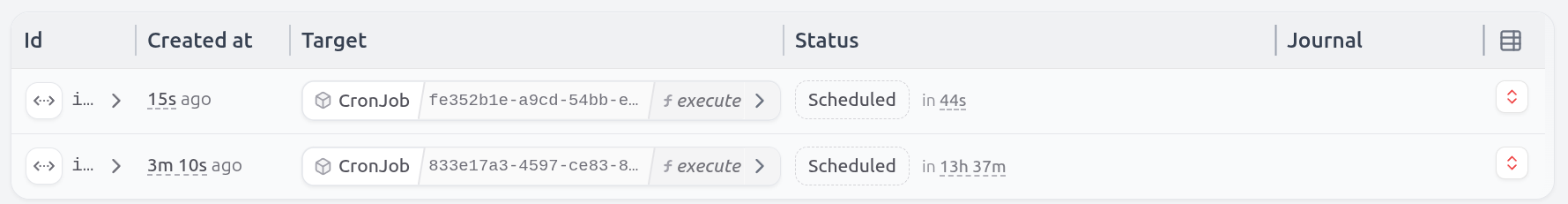

You can kill and restart any of the services or the Restate Server, and the scheduled tasks will still be there.